What it does
Fuzzyset.js creates a data structure to efficiently compute similarity scores in order to find likely misspellings in user input.
For example, if someone types "mossisippi" in a U.S. state input box, we would use this library to infer that they probably meant "Mississippi". Here's a simple interactive example:
How it works
The basic idea is to compare a search against potential matches in the dictionary and order the matches by a similarity score.
The library's functionality can be broken down into three parts:
- Calculating Similarity Scores — how do we figure out how "similar" two strings are?
- Storing the Dictionary — how do we use the similarity score to store the dictionary efficiently?
- Looking up Matches — how do we look up potential matches in that dictionary?
Calculating Similarity Scores
First, to find misspellings we want to have a way to compare strings. How do we know how similar two strings are? In this case, we can compute a "similarity score" from 0 (not similar at all) to 1 (completely similar, the same string).
The formula for cosine similarity gives us a score from 0 to 1, but to use it we have to turn strings in numeric vectors. How do we do that?
To turn a string into numeric vector, we use the _gramCounter function which counts the character substrings ("grams") in a given string:
Now that we have a way to turn strings into vectors, we can use cosine similarity to get a score between 0 and 1.
The formula for cosine similarity is:
$$\frac{A \cdot B}{\left\lVert A \right\rVert \left\lVert B \right\rVert}$$
where \(A\) and \(B\) are vectors (as shown above),
\(A \cdot B\) is the dot product of those vectors,
and \(\left\lVert A \right\rVert\) is the vector magnitude of \(A\).
To calculate the dot product, \(A \cdot B\), we just multiply the parts of each vector together and add them up:
And that is how Fuzzyset.js calculates a similarity score for two strings. Perfect matches have a score of 1, and completely dissimilar matches have a score of 0. Try it out!
Storing the Dictionary
We want to use the formula described above to match a dictionary of strings. To store strings efficiently so they can be later compared using cosine similarity, we use the following strategy:
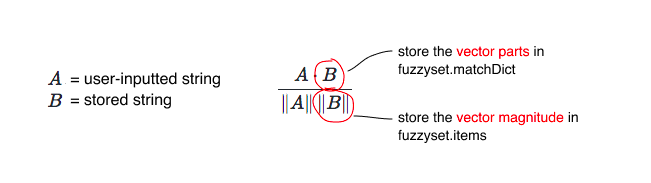 (\(A \cdot B\) and \(\left\lVert A \right\rVert\) will be calculated on-the-fly when looking up matches.)
(\(A \cdot B\) and \(\left\lVert A \right\rVert\) will be calculated on-the-fly when looking up matches.)
Here's what that looks like in practice:
How Fuzzyset stores strings
Looking Up Matches
The algorithm for looking up matches is as follows:
- Starting with
gramSizeUpper, look up potential matches with at least one gram in common (a dictionary lookup infuzzyset.matchDict), calculate the cosine similarity between the lookup string and the match, and sort the results by that score. Return all results with scores above theminMatchScore. - If
useLevenshteinistrue, compute the Levenshtein distance for the top 50 matching strings and return those results sorted by Levenshtein distance with scores above theminMatchScore. (Levenshtein distance is useful for finding misspellings where letters are out of order.) - If no results were found for steps 2 or 3, try again with the next largest gram size. (Lower gram sizes will generally create more matches of lower similarity.) Keep trying with lower gram sizes until results are found or
gramSizeLoweris reached.
Here's how this looks in practice:
Try playing around with the different parameters to see how it affects the quality of matches. For example, the useLevenshtein parameter does not provide good matches if a user hasn't typed out a whole word yet.
And that's basically the whole library! We store strings so they can be looked up quickly and compared using cosine similarity.